R for Sound Analysis Tutorial
Here I include some of the most commonly used functions for acoustic data analysis.
library(ggplot2)
library(umap)
library(seewave)
library(tuneR)
library(phonTools)
library(signal)
library(warbleR)
# Part I. Read in sound files and spectrograms ---------------------------
# We can easily read in the sound file using the following line of code
LongSoundFile <- tuneR::readWave('S11_20180319_060002.wav')
# Now we can check the structure of the resulting .wav file
LongSoundFile@left[1:5] # This returns the values of the waveform
## [1] -1038 -722 171 -148 -504
LongSoundFile@samp.rate # This is the sampling rate
## [1] 16000
# We can also read in the selection table made in Raven using the following code
SelectionTableName <- 'VirtualClusteringExample_S11_20180319_060002.Table.1.selections.txt'
SoundscapeTable <- read.delim(SelectionTableName,
stringsAsFactors = F)
# Now we want to check the structure of the table
# str(SoundscapeTable)
# head(SoundscapeTable)
# This selection table has annotations of different call types
table(SoundscapeTable$Call.type)
##
## argus bird1 bird2 female.gibbon insect1
## 7 5 5 5 5
# We can use the Raven selection table to isolate these particular sounds
ListofWavs <- lapply(1:nrow(SoundscapeTable), function(x) cutw(LongSoundFile, from=SoundscapeTable$Begin.Time..s.[x],
to=SoundscapeTable$End.Time..s.[x], output='Wave'))
# We now have a list of .wav files that were created from our Raven selection table. If we want we can save them to a local directory
dir.create('SoundFiles') # This line creates a folder in your working directory
# This loop will write the shorter sound files to the directory indicated above
for(x in 1:length(ListofWavs)){
writeWave(ListofWavs[[x]],
filename= paste('SoundFiles','/',SoundscapeTable$Call.type[x],
'_', x, '.wav',sep=''))
}
# Now we can make a spectrogram. First lets read in the .wav file
FemaleGibbonFile <- readWave("SoundFiles/female.gibbon_2.wav")
# There are many different packages that you can use to create spectrograms
# This is a spectrogram from 'seewave'
seewave::spectro(FemaleGibbonFile,flim=c(0,3))
# Lets check out spectrograms of all the signals
GreatArgusFile <- readWave("SoundFiles/female.gibbon_2.wav")
Bird1File <- readWave("SoundFiles/bird1_9.wav")
Bird2File <- readWave("SoundFiles/bird2_20.wav")
Insect1File <- readWave("SoundFiles/insect1_24.wav")
seewave::spectro(FemaleGibbonFile,flim=c(0,3))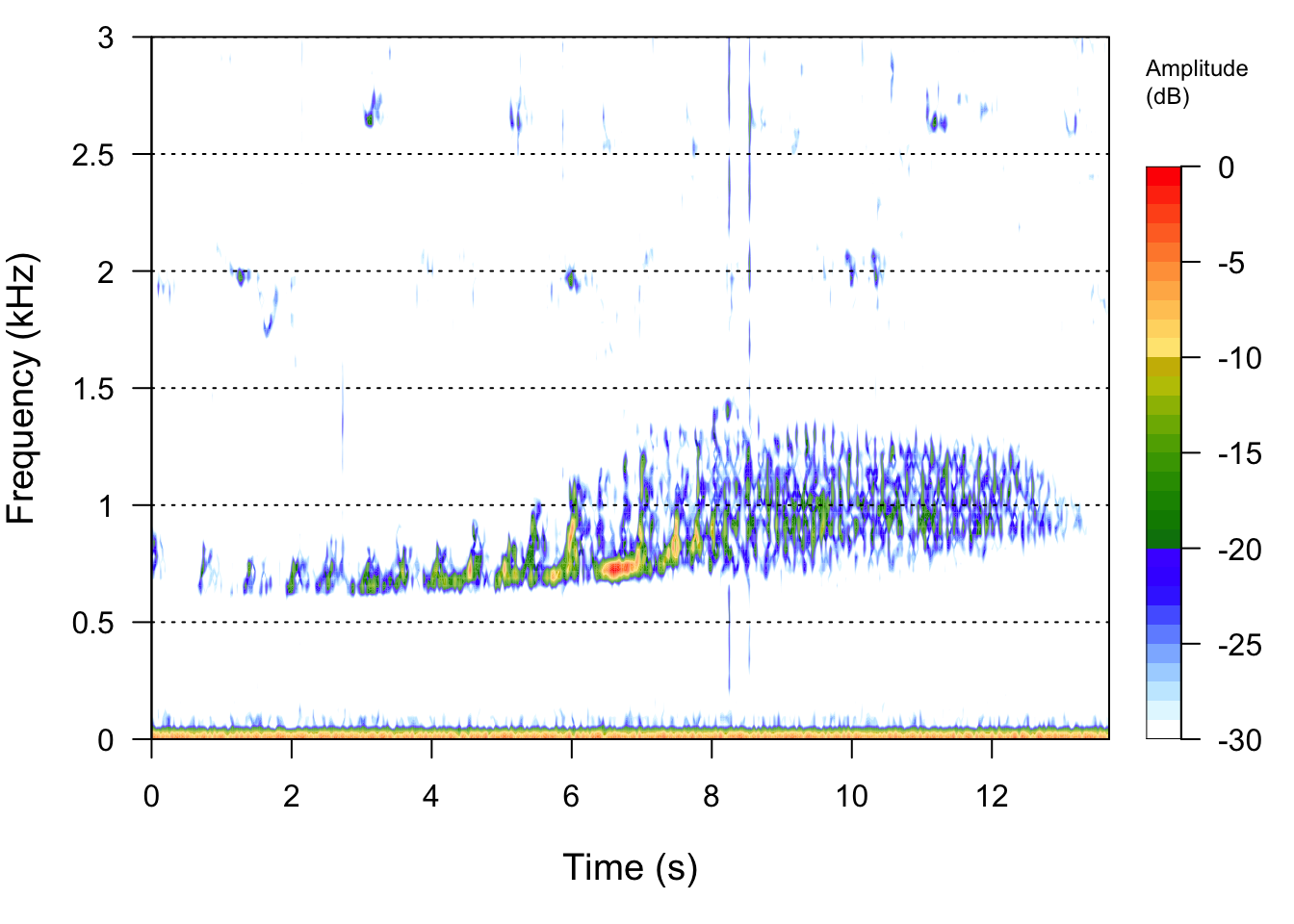
seewave::spectro(Bird1File,flim=c(0,3))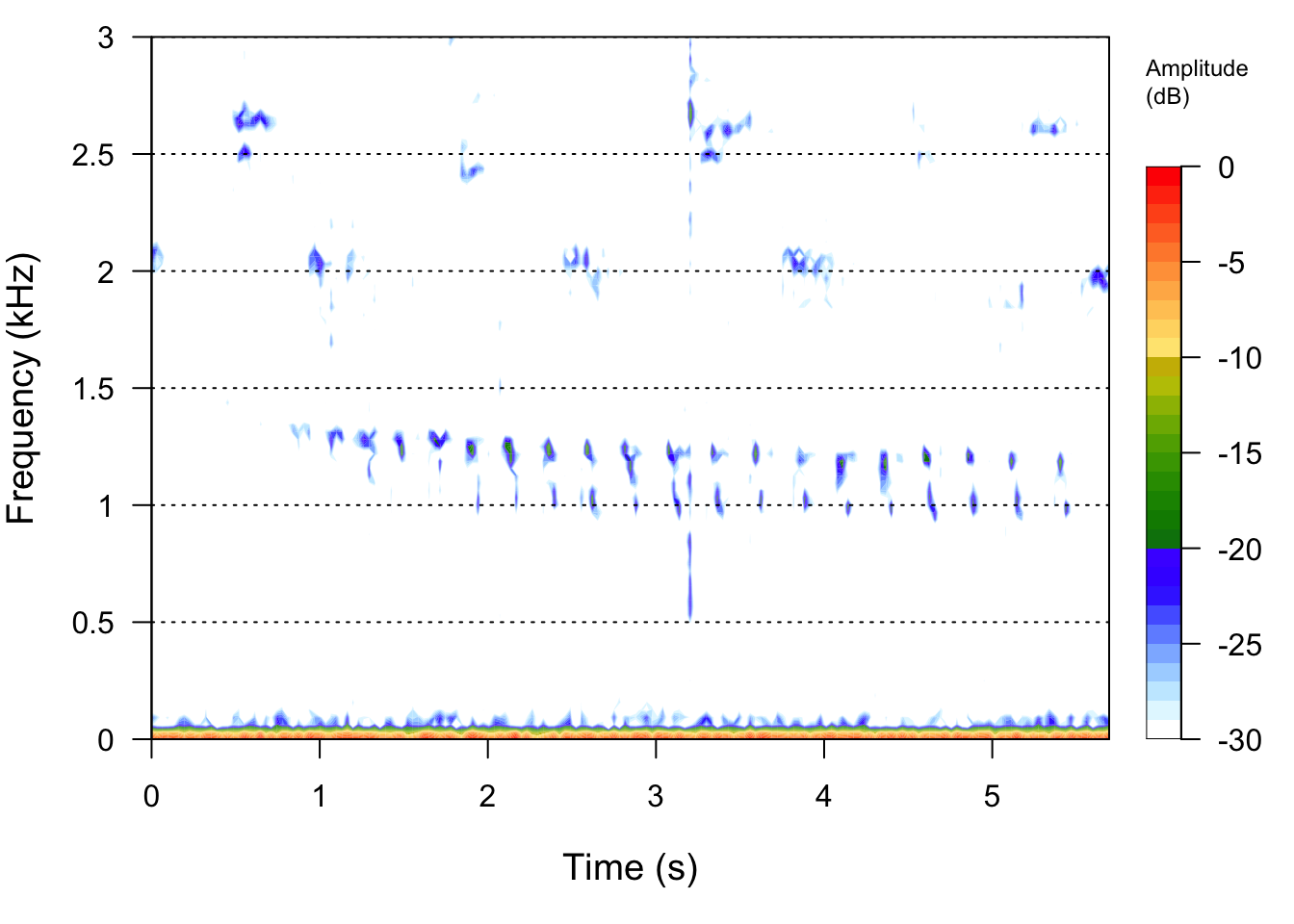
seewave::spectro(Bird2File,flim=c(0,3))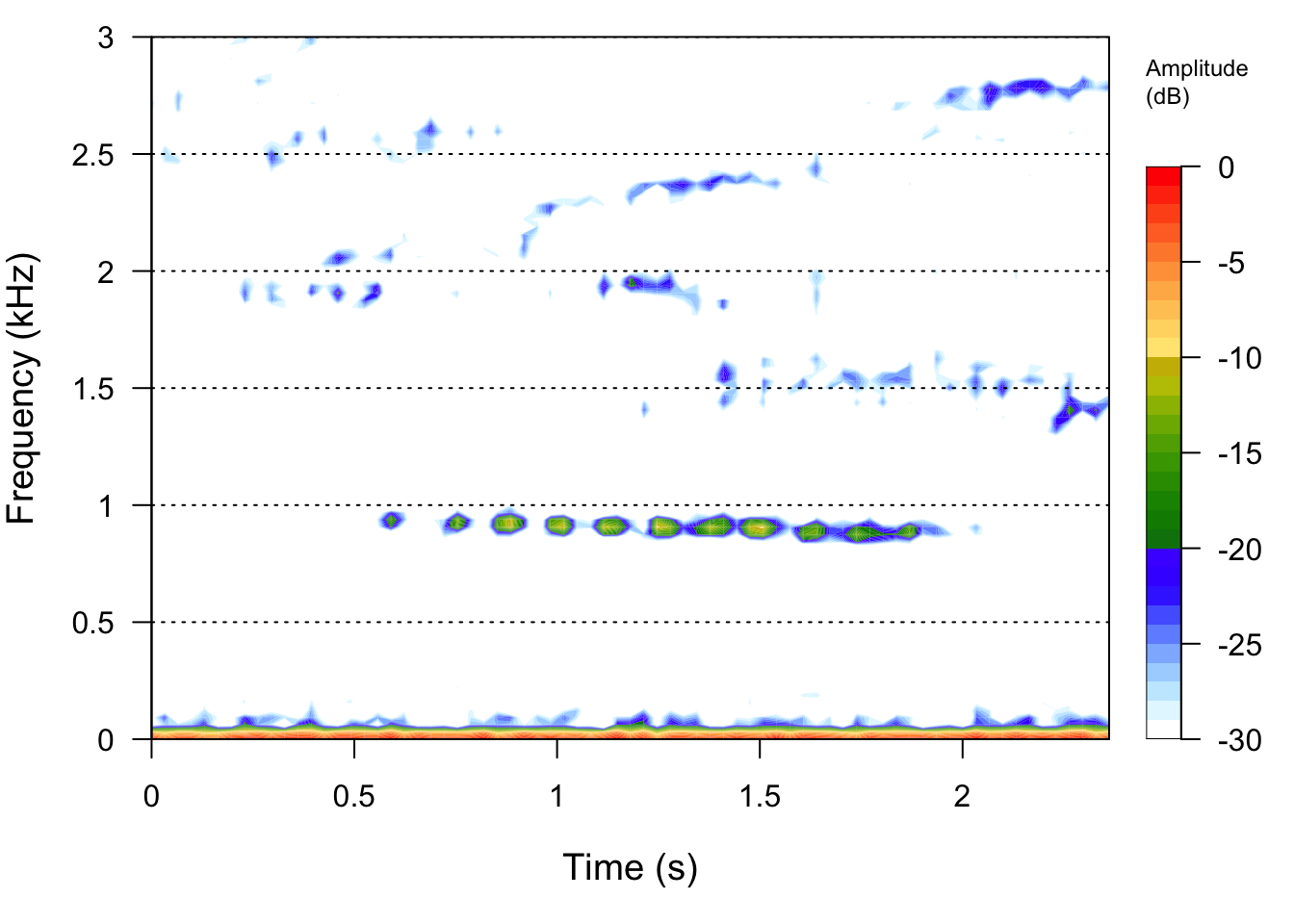
seewave::spectro(Insect1File,flim=c(3,6))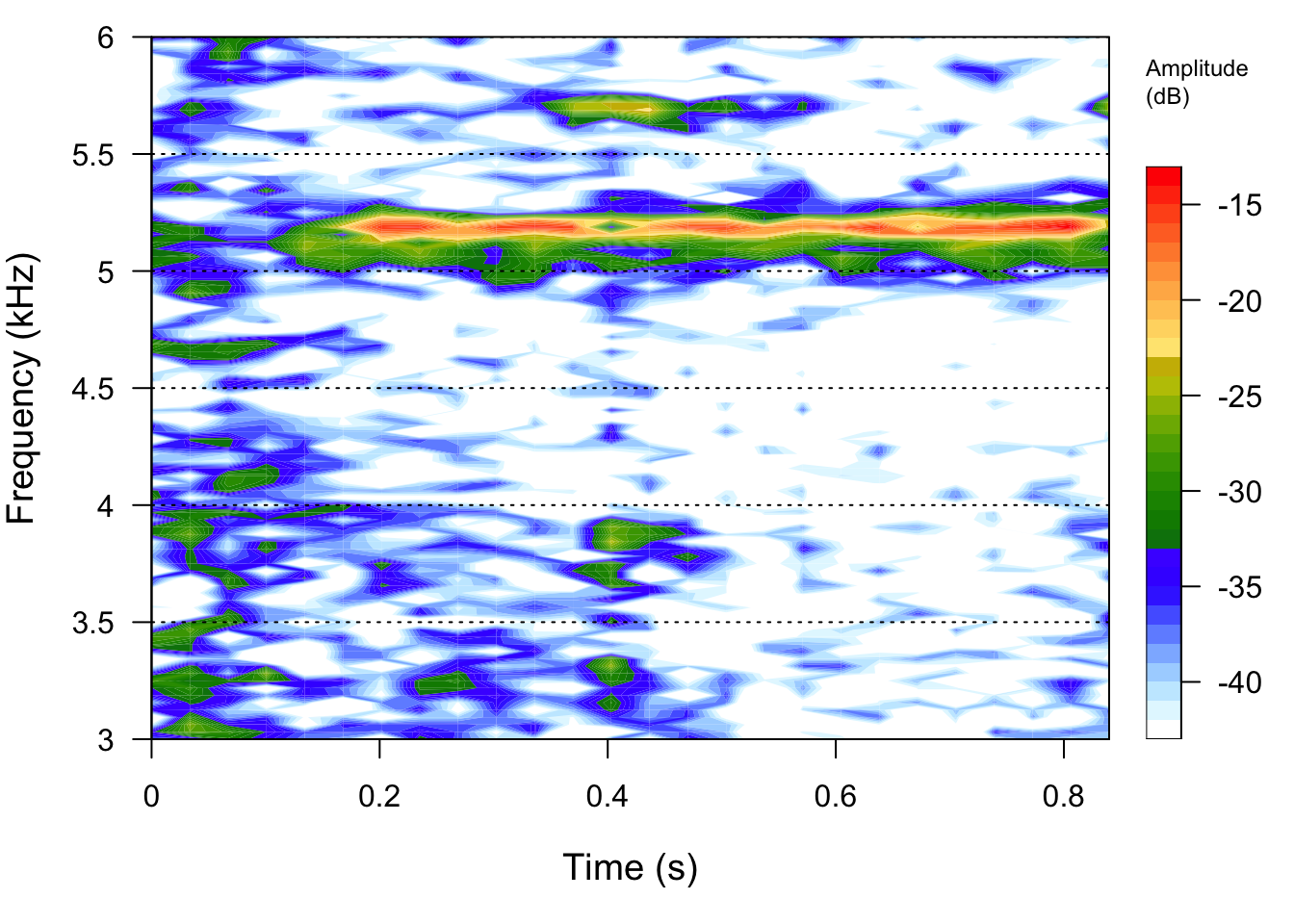
# Part 2. Unsupervised classification ------------------------------------
# Our Raven selection table also has some potentially useful features for distinguishing between call types
#str(SoundscapeTable)
# First let's try a more traditional unsupervised approach- PCA
BorneoCallTypes.pca <-
princomp(SoundscapeTable[,c(8:11)])
plot.for.BorneoCallTypes <-
cbind.data.frame(BorneoCallTypes.pca$scores [,1:2],
SoundscapeTable$Call.type)
colnames(plot.for.BorneoCallTypes) <-
c("Dim.1", "Dim.2", "Call.type")
my_plot_BorneoCallTypes.pca <-
ggplot(data = plot.for.BorneoCallTypes, aes(
x = Dim.1,
y = Dim.2,
colour = Call.type
)) +
geom_point(size = 3) +
scale_color_manual(values = matlab::jet.colors (length(unique(plot.for.BorneoCallTypes$Call.type)))) +
theme_bw() + ggtitle('Borneo call types') + xlab('pca: Dim 1')+ylab('pca: Dim 2')#+ theme(legend.position = "none")
my_plot_BorneoCallTypes.pca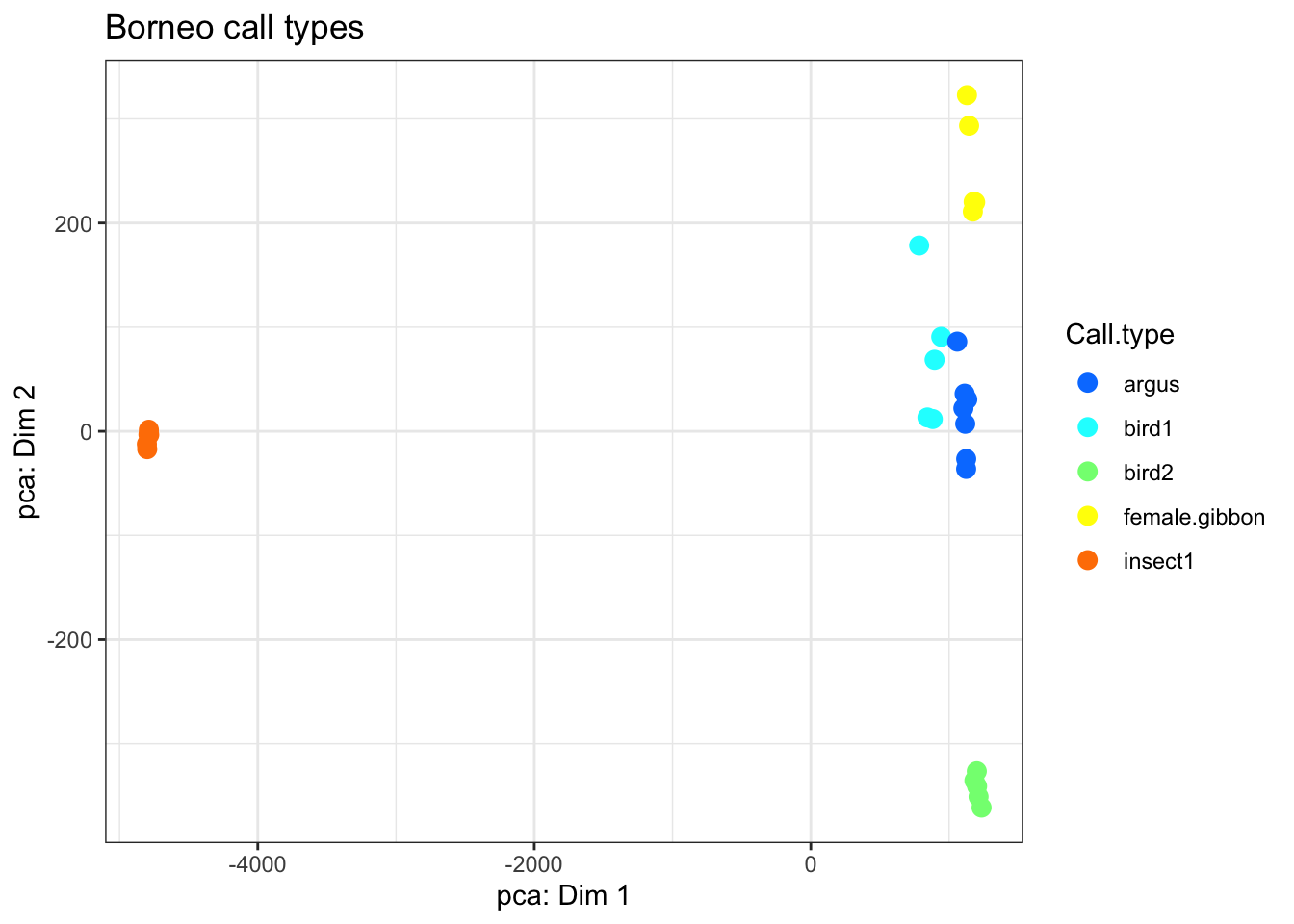
# Now we can use Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction
BorneoCallTypes.umap <-
umap::umap(SoundscapeTable[,c(8:11)],labels=as.factor(SoundscapeTable$Call.type),
controlscale=TRUE,scale=3)
plot.for.BorneoCallTypes <-
cbind.data.frame(BorneoCallTypes.umap$layout[,1:2],
SoundscapeTable$Call.type)
colnames(plot.for.BorneoCallTypes) <-
c("Dim.1", "Dim.2", "Call.type")
my_plot_BorneoCallTypes <-
ggplot(data = plot.for.BorneoCallTypes, aes(
x = Dim.1,
y = Dim.2,
colour = Call.type
)) +
geom_point(size = 3) +
scale_color_manual(values = matlab::jet.colors (length(unique(plot.for.BorneoCallTypes$Call.type)))) +
theme_bw() + ggtitle('Borneo call types') + xlab('UMAP: Dim 1')+ylab('UMAP: Dim 2')#+ theme(legend.position = "none")
my_plot_BorneoCallTypes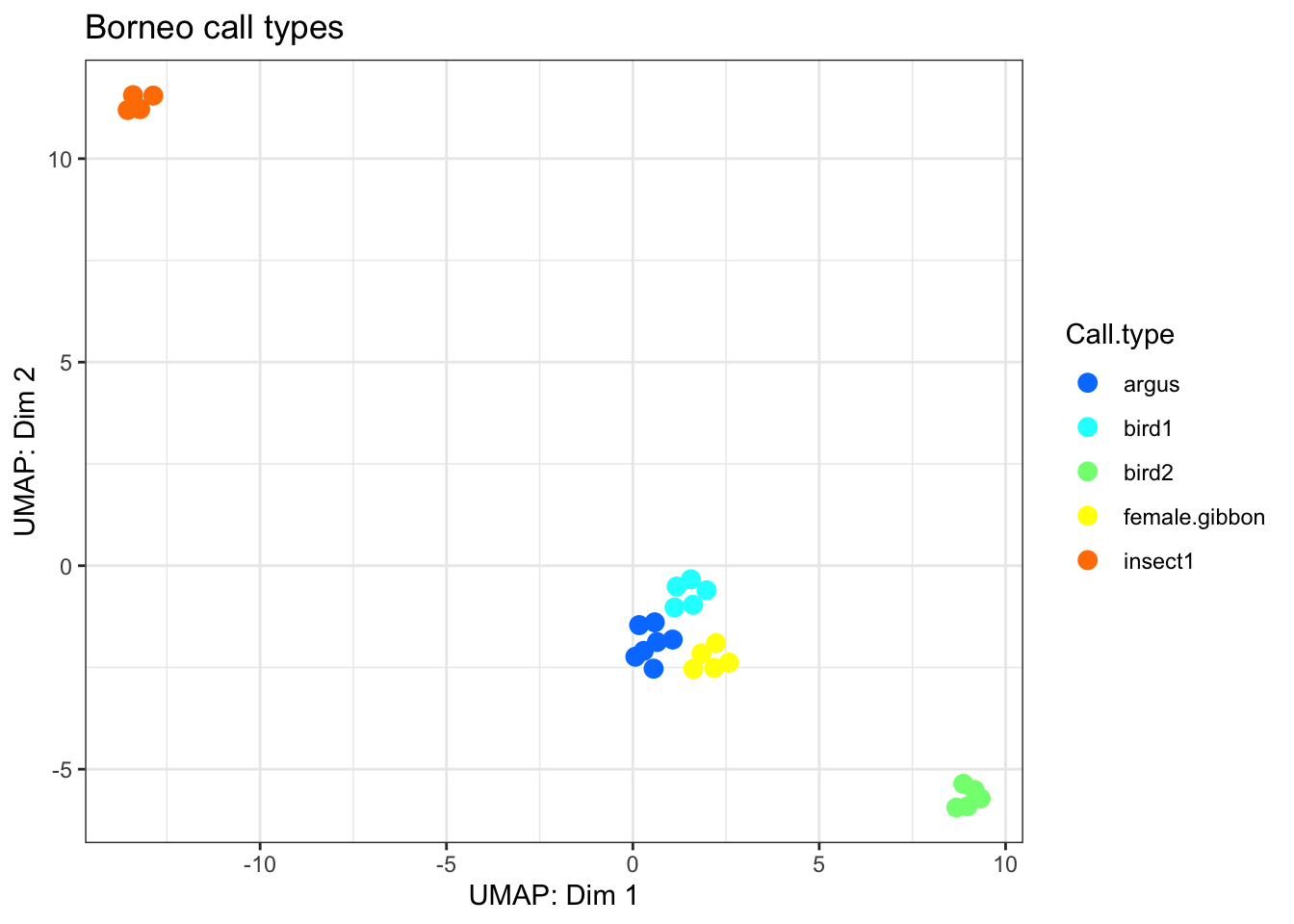
# Part 4. Supervised classification --------------------------------------
LDAdata <- SoundscapeTable[,-c(1:5)]
lda.output <- MASS::lda(
Call.type ~ .,
data=LDAdata,
center = TRUE,
scale. = TRUE,
CV = T
)
# Assess how well the leave one out cross validation did
ct <-
table(grouping = LDAdata$Call.type, lda.output$class)
# Check structure of the table
ct
##
## grouping argus bird1 bird2 female.gibbon insect1
## argus 7 0 0 0 0
## bird1 0 5 0 0 0
## bird2 0 0 5 0 0
## female.gibbon 0 0 0 5 0
## insect1 0 0 0 0 5
# Calculate total percent correct
percent <- sum(diag(prop.table(ct)))*100
percent
## [1] 100
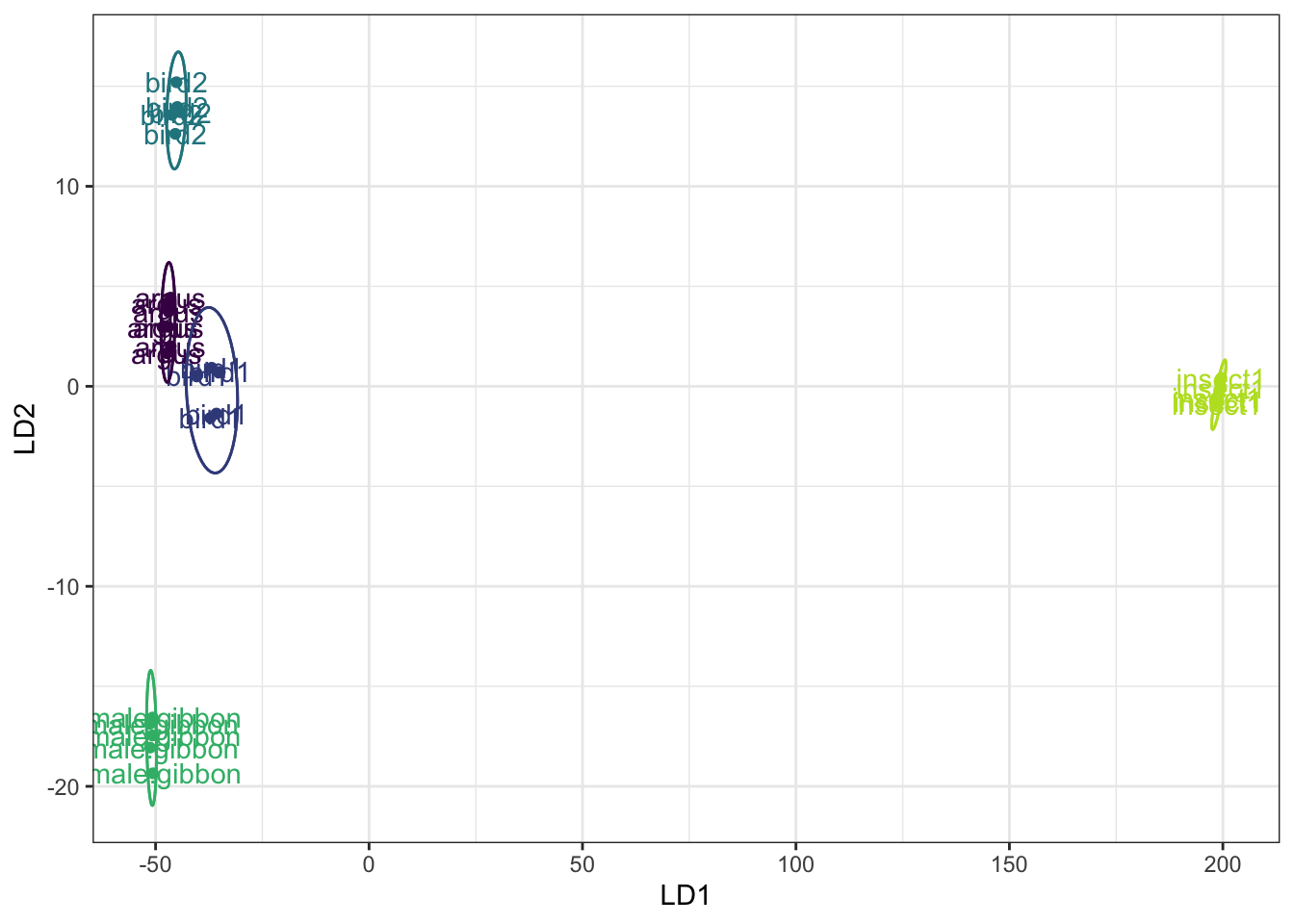
# Now we can create a biplot based on the LDA
fit.lda <- MASS::lda(Call.type ~ ., LDAdata)
class.lda.values <- predict(fit.lda)
# Combine the results into a new dataframe
newdata <- data.frame(class = LDAdata$Call.type, lda = class.lda.values$x)
# Code to create the plot
lda.plot <- ggplot(newdata, aes(lda.LD1, lda.LD2, colour = class)) +
geom_point() + geom_text(aes(label = class)) + stat_ellipse() + xlab("LD1") + ylab("LD2") +
stat_ellipse(aes(lda.LD1, lda.LD2)) + theme(legend.position = "") + theme(axis.text.x = element_text(size = 20)) +
theme(axis.text.y = element_text(size = 20)) + theme(axis.title.x = element_text(size = 20)) +
theme(axis.title.y = element_text(size = 20)) + viridis::scale_color_viridis(discrete = T, end = 0.9) +
theme(panel.grid.major = element_blank(), panel.grid.minor = element_blank(), axis.line = element_blank()) +
guides(colour = FALSE) +theme_bw()
lda.plot